Generative AI
Generative AI is a subset of artificial intelligence that focuses on creating new content.
The digital world is abuzz with a term Generative AI. We see it powering tools that craft essays, compose symphonies, and paint breathtaking vistas from mere words.
But what truly lies behind this technology? This article will unravel the essence of Generative AI, placing it within the wider family of artificial intelligence.
The AI family tree
To truly appreciate Generative AI, it helps to first understand its roots within the broader landscape of AI. We can imagine AI as a tree, with many branches.
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI): This is the trunk of the tree, the foundational concept. AI encompasses any endeavor to make computers mimic human intelligence – whether that's understanding our speech, mastering complex games, or making intricate decisions. The overarching ambition is to build systems capable of perception, reasoning, learning, and problem-solving.
-
Machine Learning (ML): Growing from this trunk is a major branch called Machine Learning. Instead of meticulously programming a computer for every conceivable task, ML allows systems to learn directly from data. By feeding an ML model vast quantities of information, it begins to discern patterns and can then make predictions or decisions, all without explicit instructions for each specific scenario. Think of how your email service learns to filter spam by analyzing countless examples of unwanted messages.
-
Deep Learning (DL): Further out on the ML branch, we find Deep Learning. This specialized technique employs structures known as artificial neural networks, which are loosely inspired by the interconnected neurons in our own brains. These networks possess multiple layers (hence "deep"), enabling them to unearth incredibly subtle patterns from colossal datasets. Deep Learning is the engine driving many of today's most impressive AI achievements, from recognizing faces in photos to understanding spoken language, and, crucially for our case, it's a key enabler of Generative AI.
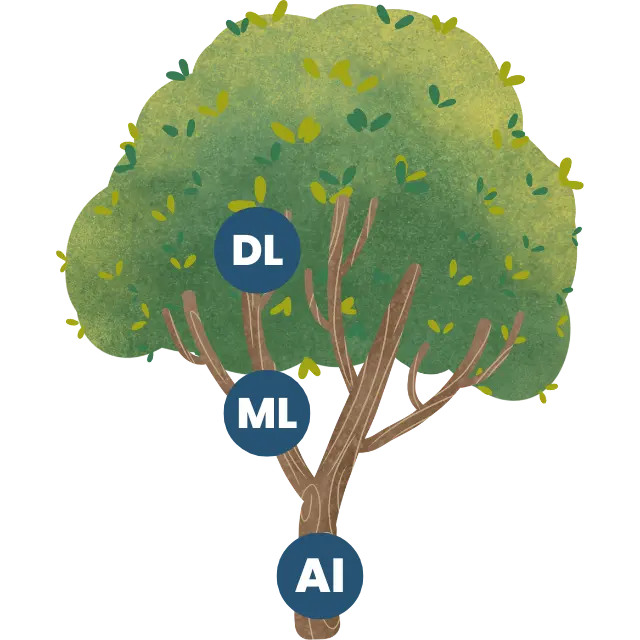
So, we have AI as the overarching goal, Machine Learning as a method to achieve it through data, and Deep Learning as a powerful technique within Machine Learning.
For video learners, here's a great video that explains those concepts in a visual way.
So, what is generative AI?
Generative AI distinguishes itself with a unique capability - it creates. While other AI systems might be adept at classifying information (like identifying whether an image contains a cat or a dog) or predicting future outcomes (such as forecasting stock prices), Generative AI is all about bringing something entirely new into existence.
This act of creation isn't limited to a single medium. Generative AI can weave words into articles, compose poetry, draft code, or email responses. It can conjure realistic photographs, illustrations, or sculpt 3D models.
Its creative reach extends to the auditory realm, where it can compose original musical pieces, synthesize human-like voices, or design unique sound effects. It can even animate short video clips or generate synthetic datasets, which are invaluable for training other AI models.
The defining characteristic here is originality. While Generative AI learns from a vast pool of existing data, its output isn't a mere imitation or a cut-and-paste job. Instead, it synthesizes novel content, producing creations that, while influenced by what it has learned, are genuinely new.
How does generative AI learn to create?
The journey from data to original creation is a sophisticated one, rooted in the principles of Deep Learning. Imagine wanting to teach an AI to paint like Van Gogh. You wouldn't just show it one painting; you'd immerse it in thousands of his works. The AI model doesn't "see" these paintings in the human sense.
Instead, it meticulously processes the underlying data – the specific hues, the texture of the brush strokes, the arrangement of shapes, the overall composition. From this ocean of information, it begins to learn the intricate patterns, the statistical relationships, and the stylistic nuances that define Van Gogh's unique artistic signature.
Through this intensive training, the model constructs an internal, incredibly complex mathematical representation of the artistic style. This isn't a simple gallery of stored images but a deeply encoded understanding – an "essence" – of Van Gogh's art.
Now, if you prompt this trained model, perhaps asking for "a painting of a bustling futuristic city at twilight, in the style of Van Gogh", it draws upon this learned essence. It doesn't copy an existing starry night or a previous cityscape. Instead, it synthesizes a new image that fulfills your request while authentically reflecting the swirling skies and vibrant colors characteristic of the master painter.

This act of synthesis, of creating something novel based on learned patterns, is the essence of Generative AI.
Differentiating generative AI from its relatives
The world of AI is filled with terms that can sometimes blur together – AI itself, Machine Learning, Deep Learning, and even specific types like Large Language Models (LLMs). It's important to see how Generative AI carves out its own distinct niche within this family. The following table offers a clear comparison of the key concepts in the AI landscape:
| Concept | Core idea | Primary goal | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| AI | Machines mimicking human intelligence. | To perform tasks that typically require human intellect. | A self-driving car, a virtual assistant, a chess-playing program. |
| ML | Systems learning from data without explicit programming. | To identify patterns and make predictions or decisions based on data. | Spam filters, recommendation engines, fraud detection. |
| Deep Learning | A type of ML using multi-layered neural networks. | To learn complex patterns from vast amounts of data for sophisticated tasks. | Image recognition, natural language understanding, speech recognition. |
| Generative AI | AI that creates new, original content based on learned patterns. | To produce novel text, images, audio, video, or data. | Creating a new image from a text description, writing a poem. |
| LLM | A type of Generative AI specialized in understanding and generating human-like text. | To process, understand, and generate coherent and contextually relevant text. | Chatbots (like ChatGPT), text summarization, language translation. |
This table highlights that Generative AI isn't a replacement for these other concepts but rather a specific capability or category within the broader AI field.
It often leverages the power of Deep Learning to achieve its creative ends. Large Language Models, which have recently captured so much attention, are a very prominent and powerful form of Generative AI, but they are usually tailored to the domain of text. Generative AI's creative canvas, however, is far broader, encompassing images, sound, and more.
Why the sudden surge in popularity?
While the foundational ideas behind Generative AI have been percolating in research labs for years, a confluence of factors has recently catapulted it into the mainstream spotlight. It’s as if several key ingredients finally came together to bake this impressive cake.
Firstly, the sheer volume of data available for training these models is unprecedented. The internet, with its endless repositories of text, images, audio, and video, has become an immense digital library from which AI can learn.
Secondly, there have been remarkable breakthroughs in the algorithms themselves, particularly within Deep Learning. New architectures, such as the transformer models that form the backbone of many LLMs, and innovative techniques like diffusion models for image generation, have made AI systems significantly more potent and efficient.
Alongside these algorithmic leaps, the necessary computational power has become more accessible. Training these enormous models requires immense processing power, and the widespread availability of powerful Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) has made this once-prohibitive task feasible.
Finally, the technology is no longer confined to academic circles. A growing number of user-friendly tools and platforms are putting the power of Generative AI into the hands of a much wider audience, sparking a wave of experimentation and innovation.
What can generative AI actually do?
The practical applications of Generative AI are blossoming across a surprisingly diverse array of fields, limited perhaps only by our imagination. In the realm of content creation, it's already drafting articles (don't worry, not this one), composing marketing slogans, writing scripts for videos, and generating engaging social media updates.
For artists and designers, it offers a new palette, enabling the creation of unique images, original musical scores, assets for video games, and even novel product designs.
The world of software development is also being reshaped, with Generative AI assisting in writing code, identifying bugs, and even generating technical documentation.
It's paving the way for deeply personalized experiences, from news feeds curated to individual tastes to educational programs that adapt to a student's unique learning pace.
Even scientific research is benefiting, as AI can help generate hypotheses, design complex experiments, or create synthetic data to simulate scenarios that would be difficult or impossible to test in the real world.
And in entertainment, it’s being used to develop dynamic game narratives, craft stunning special effects, and bring virtual characters to life with unprecedented realism.
This list is not exhaustive; it's a snapshot of a rapidly evolving landscape where new uses are discovered almost daily.
The road ahead
The journey of Generative AI is just beginning, and it has the potential to significantly amplify human creativity, supercharge productivity across industries, and foster groundbreaking innovation. By democratizing the tools of creation, it can empower individuals to express ideas in ways previously unimaginable. It can help us tackle complex problems by offering new perspectives and solutions, and it may unlock entirely new forms of artistic and scientific endeavor.
However, as with any technology of such transformative power, the road ahead also presents challenges and demands careful ethical navigation. The ability to create highly realistic but entirely fabricated content like "deepfakes", raises serious concerns about the spread of misinformation and its potential for malicious use.
Furthermore, AI models learn from the data they are fed, and if this data reflects existing societal biases, the models can inadvertently perpetuate or even amplify these prejudices in their outputs. Thorny questions also arise around copyright and intellectual property: who owns AI-generated content, and how should the use of copyrighted material in training datasets be handled? And, naturally, there are discussions about the potential impact on professions that traditionally rely on human content creation.
Conclusion
Generative AI is far more than a fleeting technological trend; it signals a profound shift in the capabilities of artificial intelligence. It marks a point where machines are not just analyzing data or following instructions but are actively participating in the creative process itself, transforming learned patterns into novel and often surprising outputs.
By understanding its fundamental nature as an engine of creation, and its place within the broader story of AI, we can better appreciate its transformative potential. As Generative AI continues its rapid evolution, it is poised to redefine how we work, how we express ourselves, and how we interact with the increasingly intelligent digital world around us, heralding a truly new era of creation.
If you want to dive even deeper, you can watch the following videos: